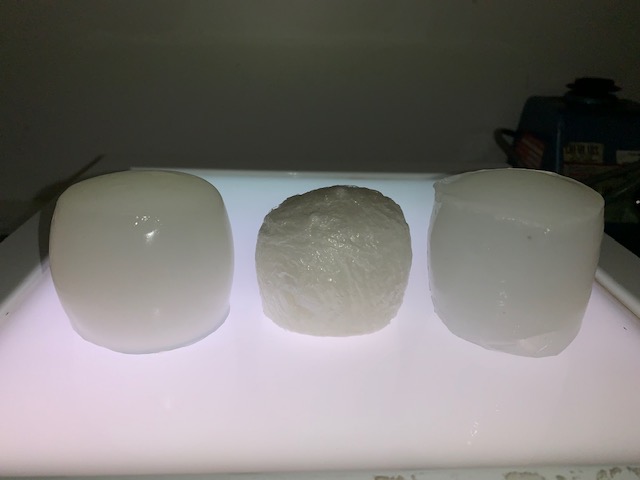

A simple cylinder shape was selected to create 3D bio-polymer prototypes. Simplicity of form is desired at this stage to make variations evident. The same 3D bio-polymer formula was manipulated via different drying methods; aqueous storage, freeze drying and air drying. We are testing for moisture holding capacity and shrink rate.
The samples cast with some distortion; external shrinkage causing bulging due to chemical cross-linking of the polymer. Sample (a) and (c) were soft and nice to carve. The freeze dried material was porous and open; possibly useful for seeding with other materials.
Only the structure of the freeze dried sample (b) is visible under microscopy. A combination of films and fibres were observed.
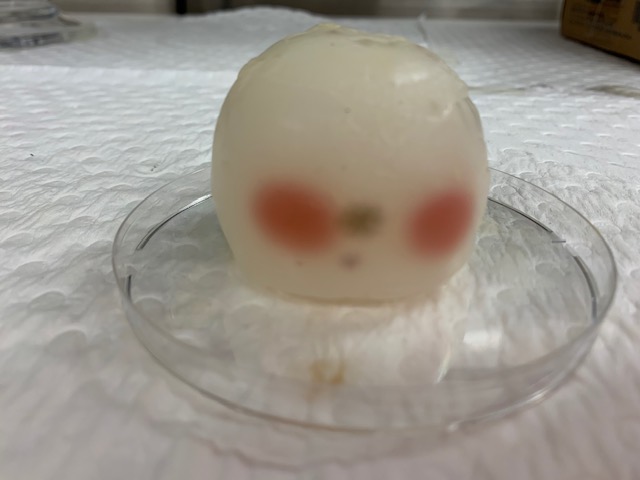
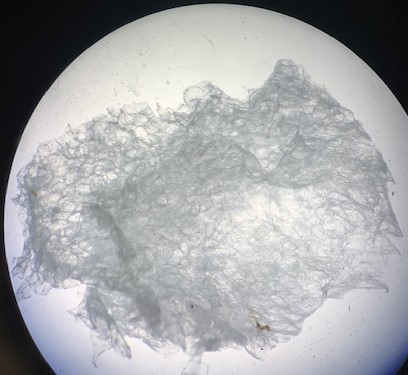
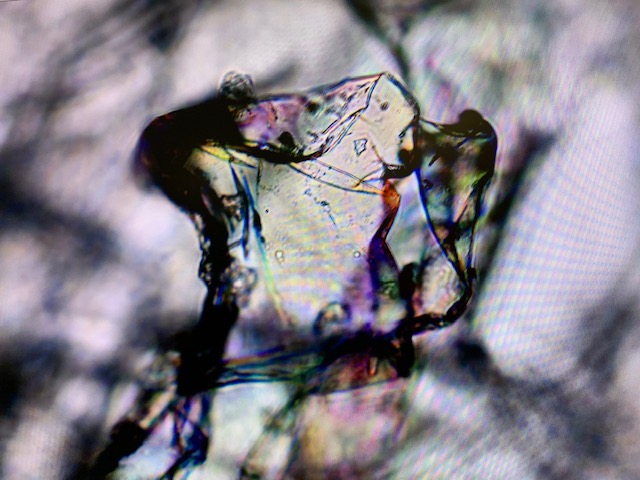
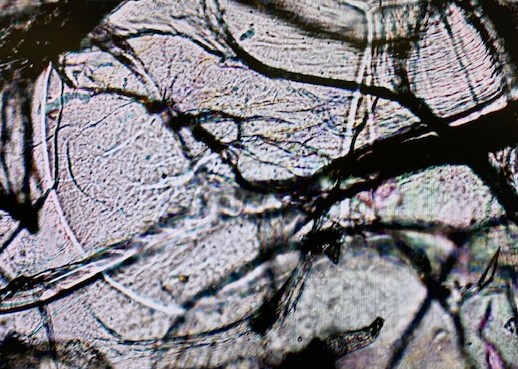

Air dried, sample (c) continued to shrink and bulge. Microbial contamination is apparently a ‘good thing’ as it evidences the ability of the polymer to support life.
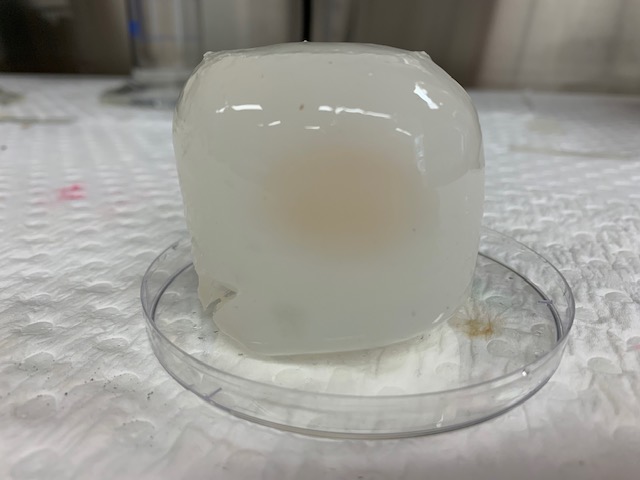

Aqueous environment, sample (a) showed markedly less shrinkage and was also contaminated.
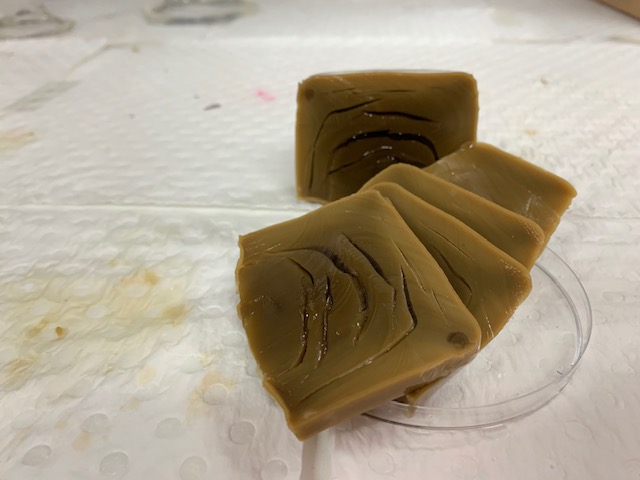


Unrefined experimental natural seaweed 3D bio-polymer was produced toward the goal for zero waste and less energy consumption.